
$ ip addr show eth0Ħ: eth0: mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000 To list all network interfaces, use ip a command or specify the name of the network interface as shown below. Besides GUI network manager based on the Linux distribution, there is a set of common CLI commands that are mostly supported across different distributions by default.
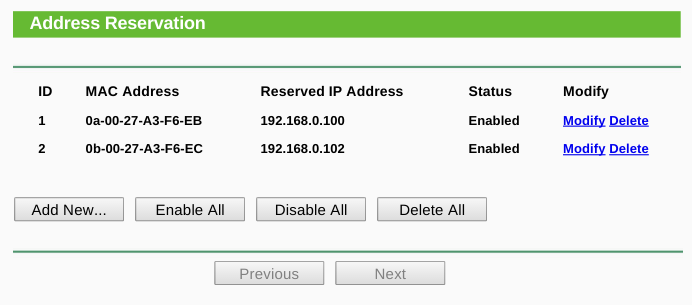
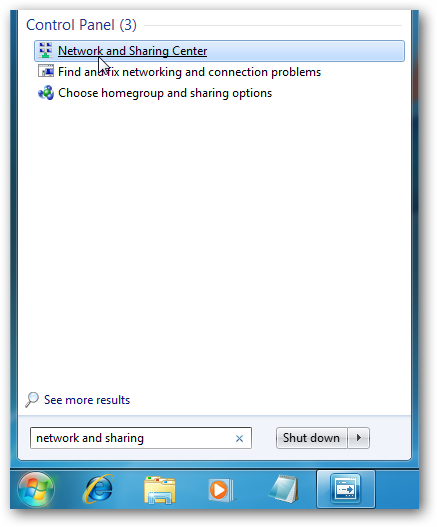
Linux offers a range of options to check your system’s IP address. Below is a screenshot showing network details from Settings app: Linux Then go to Network & Internet -> Select your connection type (here it is Wi-Fi) -> Hardware Properties. For this, open the Control Panel and go to Network and Internet -> Network and Sharing Center -> Connections: / -> Details. Here’s an example: Network and Sharing CenterĪnother method by which you can find your system’s/network adapter’s IP address is by opening Network and Sharing Center. There could be multiple IP addresses in that list based on your connectivity like ethernet, Wi-Fi, etc.
#Ip address menu windows
When you run the command ipconfig on Windows’ Command Prompt, it will list down all the network adapters found on your Windows system. Because IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority) assigns a unique range of addresses across different countries. Since addresses are unique across the Internet, it also determines the location of the devices from where it is connecting to. Whereas external IP addresses are globally accessible on the internet.
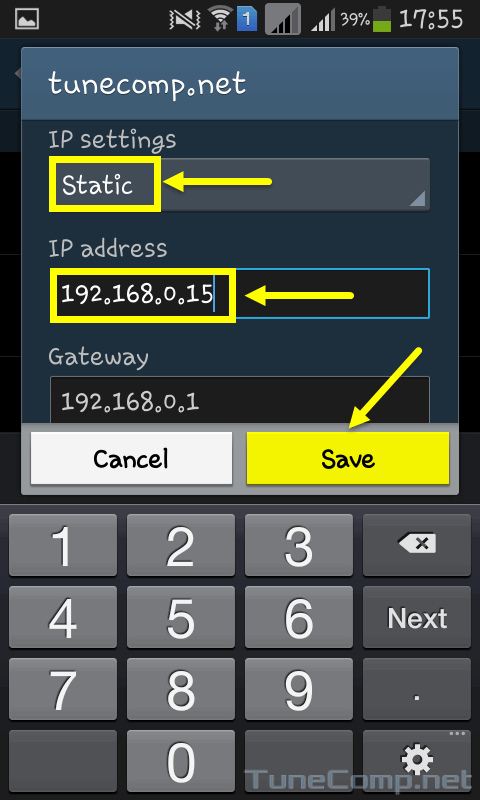
Additionally, the same internal IP can be used across two different network subnets, so they are not necessarily unique identifiers. Devices with these addresses are not reachable globally and are accessible within the LAN only.
Internal IP addresses are for messaging and connectivity within the internal network. IPv6 addresses support a much larger range and are formatted like y:y:y:y:y:y:y:y where each y is a segment that can range between 0 and FFFF in hexadecimal like 2001:0db8:0001:0000:0000:0ab9:C0A8:0102.Īn IP address helps in location addressing of the connected device and for network interface identification.Īlso, we need to remember that each connected device can have two types of IP addresses: The address of each device in an IP subnet (a kind of subset of complete IP range) should always be unique means no two devices on the same subnet can have the same IP address, otherwise, it will cause an IP address conflict.įor IPv4, its format can be 4 octets like x.x.x.x where each octet is 8 bits or 0 to 255 in decimal. One of the most common and popular examples of a network built on IP addresses is World Wide Web and Internet. View or change the current HTTPS setting.An IP (Internal Protocol) address is a unique identifier that identifies a device on the internet-connected to the TCP/IP protocol and enabled communication over it. View or change the backup DNS server addresses. View or change the current DNS server address. View or change the current WINS server address. When enabled, the printer can be monitored and managed remotely using a Web browser. Note: Yes is the factory default setting.Įnable the built-in FTP server, which lets you send files to the printer using File Transfer Protocol.Įnable the built-in Web server (Embedded Web Server). Specify the Zero Configuration Networking setting. Specify the BOOTP address assignment setting.

View or change the current TCP/IP netmask. It also sets Enable BOOTP and Enable RARP to Off on systems that support BOOTP and RARP. Note: Manually setting the IP address sets the Enable DHCP and Enable Auto IP settings to Off. View or change the current TCP/IP address.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
